 “Things are the way they are because they have been designed to be this way,” a friend of mine said. “It’s all about preserving The Pyramid.”
“Things are the way they are because they have been designed to be this way,” a friend of mine said. “It’s all about preserving The Pyramid.”
What’s The Pyramid? Let me tell you…
“The Pyramid” (according to my friend) is a method of social, economic and political organisation that is at the core of every human civilisation from the Egyptians to Hindus to Monarchies to Capitalism.
All the big political conflicts come down to one thing: The Pyramid.
Conflicts are either initiated by people on top pulling strings to preserve or expand the present Pyramid; or conflicts are initiated by revolutionaries who disagree with the structure and seek to turn The Pyramid up-side-down.
As I thought through history, I realised my friend was right. The English and Spanish Conquest of the Americas, India, China… We seize land to expand our pyramid. We seize resources to secure our pyramid. We take down any leaders who don’t agree to it’s rules. We call anyone who challenges the Pyramid a “terrorist” and “national threat”. Why? Because they really are a threat to this hierarchy – and the people at the top do not like that.
From the Egyptians:
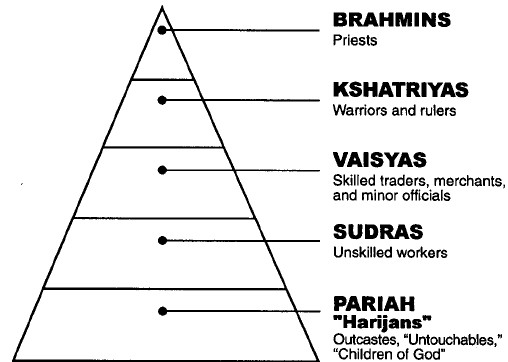
 To the Hindu caste system:
To the Hindu caste system:
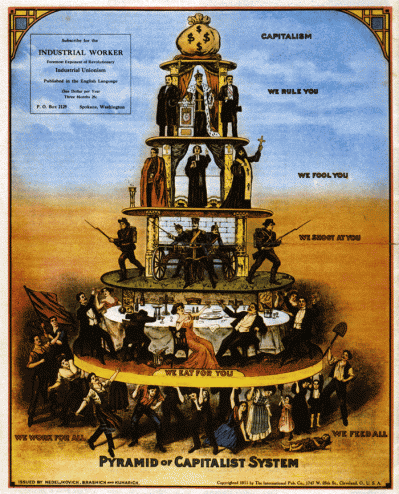
To Capitalism today…

Globalisation has seen the pyramids of once isolated civilisations join together to create an even bigger pyramid. And as the upper and middle class grows, so does the lower class, hence as our global population rapidly expands, so does The Pyramid. The rich get richer as the poor get poorer.
In the global pyramid, the top 0.5 billion earning over $20,000 a year (of which many earn far more, and a small number earning far far more than that) while 60% of the world’s population live on less than $2 a day.
The pyramid of wealth distribution looked at in another way shows the top 1% taking 2/3rds of the US national income…
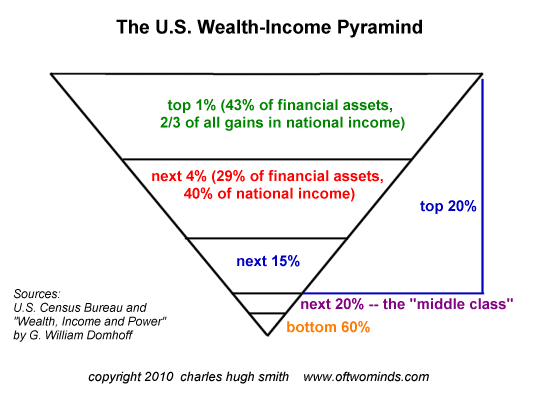
How is such inequality allowed to persist?
Through a carefully constructed system that involves a “social distribution of knowledge” [1]. We educate some (the children of the monetarily rich) to make the system work for them, and educate others (the children of the not-so-money-rich) to work for the system.
Those in power know the formula: give people a reason to live (eg through career path or religion or an ideology) and educate them enough for their societal roles. No more, no less.
The system teaches people to obey authority, not to question it. It encourages conformity, a docile acceptance of the status quo.
According to my friend’s theory, all the “evils” of the world are there for a reason: to maintain The Pyramid. This includes:
- Poverty is there because a massive base is needed to support the weight of the top.
- War is there because it secures the resources required to make weapons and keep the system running as those at the top require.
- Lack-of-education is there because in the social distribution of knowledge, not everyone needs to know stuff. All you need to know is what your role requires you to know, no more, no less.
- Religion is there because it gives people a purpose. It explains the unknowns, it controls the masses, and it gives people hope for a better life next time round – be it up in heaven or in one’s reincarnation.
- Debt is there because it contracts a permanent slave of those people and countries who work to repay it.
The destructive cycle is this: (1) as we seek to join the upper class or move up the middle classes (a good thing), we inadvertently (2) increase the lower class – not such a good thing if this means 12 hour work days behind a sewing machine. Then, (3) as the base of the pyramid increases, so does poverty (families have less food and less land to provide), and (4) as poverty increases, education decreases and people have more babies, causing (5) the global population continues to explode and (6) as the earth’s resources recede it seems inevitable that, at some point in the future, billions of people’s lives are going to be lost.
Should we challenge The Pyramid? Maybe. But to be honest I’m not sure that we can.
What happens when someone challenges the authority of The Pyramid? They get taken down. Just look what they are doing to Julian Assange!
History has shown Animal Farm scenarios time and time again: revolution upon revolution. When oppressive humans are kicked off the planet and animals declare themselves equal, it’s only a matter of time before pigs (or some other animal) will rise up and become the new oppressor.
The Pyramid has been torn down and built back up by a numerous groups who then take the place of the new rich and powerful. Whoever wins the battle replicates the model’s inequalities, and rewrites history to produce a new “social distribution of knowledge.” It’s an endless cycle.
Geez this is depressing. Where’s my Christmas spirit? Don’t get me started on Christmas… the capitalistic “Christian” tradition that is based on a pagan holiday inadvertently idolizing the “God” that declared “He” never wanted to be idolised. Ah sorry, I shouldn’t write it off like this. It is a lovely family time. I’ll try to uplift my words from here on…
If we can’t fight The Pyramid, should we embrace it? Maybe. Maybe there are ways of making it work without the above evils, I’m not sure.
Is inequality ok? Maybe. It’s impossible for everyone to be equal. And unappealing – diversity makes the world a more interesting place. And whose to say that the rich people are “rich”? Are those at the top of the pyramid “better off” than the people at the bottom? Life can be pretty boring if you have everything without the challenge. The poor might be much richer in different ways…
But it can’t be denied that it’s pretty shit that two-thirds of the world have no place to shit.
Maybe it’s best to live one’s life somewhere in the middle. Probably myself and most of you think of ourselves as somewhere in the middle (although earning more than $20k pa places us in the upper).
Even in the top segment of the pyramid if you have a mortgage and particularly if you have children, then choices become even more limited – we are culturally molded to work for the system. I wonder how many people at the very very top of The Pyramid are even consciously aware that they are creating or perpetuating it?
Is there anything wrong with being a cog in this wheel? No. I guess not – as long as you are happy. What if this happiness is just an illusion? Maybe living in an illusion is the best place to be. Should we be putting our efforts into finding ways to make the pyramid work for us? Maybe. But maybe not. Alternatives may exist, I’m not yet sure.
In sum, things are the way they are because they have been designed this way. Poverty, religion, education systems, health-related issues – all of our problems are (at least in part) designed to serve the powerful and preserve The Pyramid. If you want to address these problems in a way that is real and sustainable, then it will be useful for you to consider the power hierarchies within The Pyramid, and engage with those in decision-making positions to make changes toward more just institutions and hence a more just world.
When my friend first shared this theory I protested, now I’m coming around.
More on The Pyramid? Check out the sequel blog post Rethinking “The Pyramid” – do alternatives exist? and blog entries tagged “The Pyramid“.
Pictures:
I have a habit of grabbing pictures off Google Images and not recording the copyrights… if anyone would like me to acknowledge their work where I haven’t please do let me know.
References:
[1] The Social Construction of Reality, Berger and Luckmann 1966



 To the Hindu caste system:
To the Hindu caste system:



 Which Ted? Ted from How I Met Your Mother, or Ted-Talks? While both are wonderful sources of inspiration, today I will using the former to introduce “Narratology”.
Which Ted? Ted from How I Met Your Mother, or Ted-Talks? While both are wonderful sources of inspiration, today I will using the former to introduce “Narratology”.